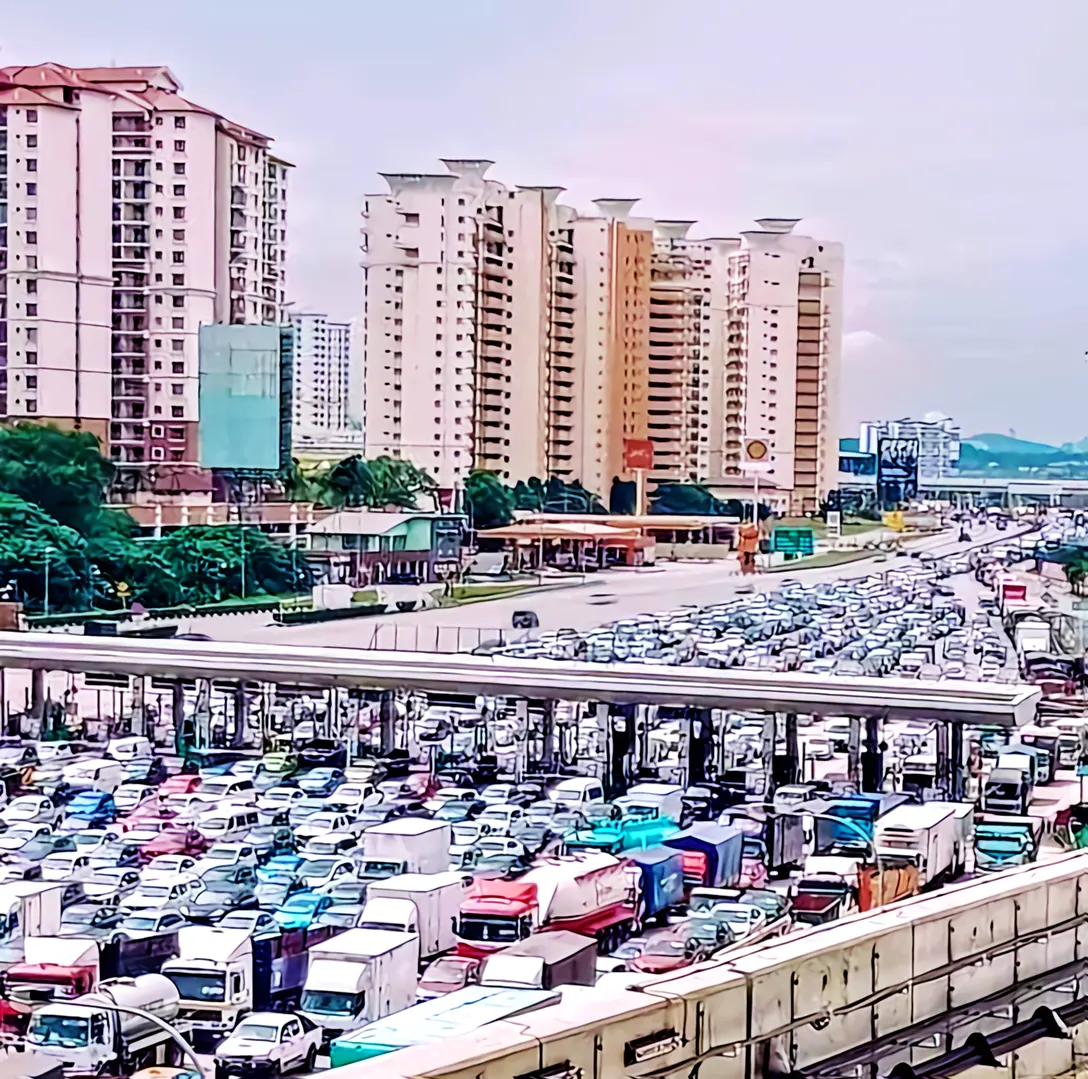
Sungai Besi Toll Plaza is one of the key entry points to the bustling city of Kuala Lumpur, it has played a crucial role in shaping the nation’s connectivity, economic growth, and urban development.

Address: 43300 Seri Kembangan, Selangor. View on Google map.
The Sungai Besi Toll Plaza stands as a testament to Malaysia’s commitment to modernizing its transportation infrastructure.
It was established in the early 1980s as part of the Kuala Lumpur–Seremban Expressway (KLSE).

At that time, Malaysia was experiencing rapid urbanization and industrialization, leading to increased traffic congestion and the need for efficient transportation networks.
The Sungai Besi Toll Plaza was strategically positioned at the southern entrance to Kuala Lumpur. It served as a gateway for travelers coming from the south, including those commuting from Seremban and other neighboring towns.
The plaza facilitated the movement of people, goods, and services into the heart of the capital city.

The toll collection system was introduced to manage traffic flow and generate revenue for highway maintenance and expansion. Vehicles passing through the plaza paid toll fees based on their class (cars, buses, lorries, etc.).
The revenue contributed to the continuous improvement of the KLSE and other highways.
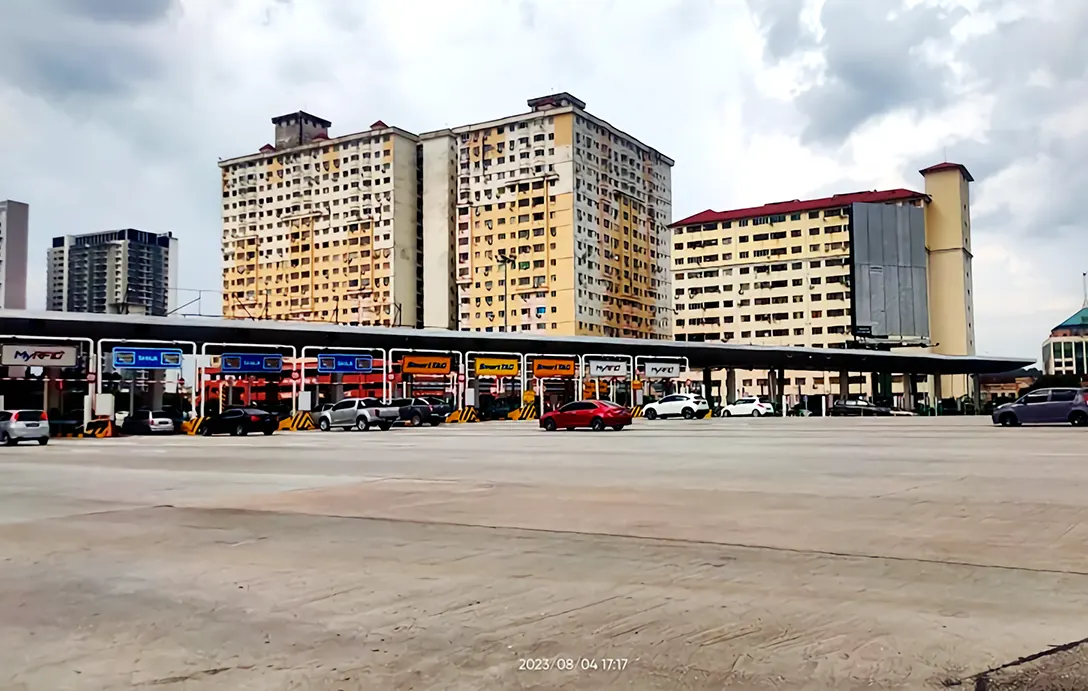
Over the years, the Sungai Besi Toll Plaza has witnessed significant technological advancements and upgrades including the Electronic Toll Collection (ETC).
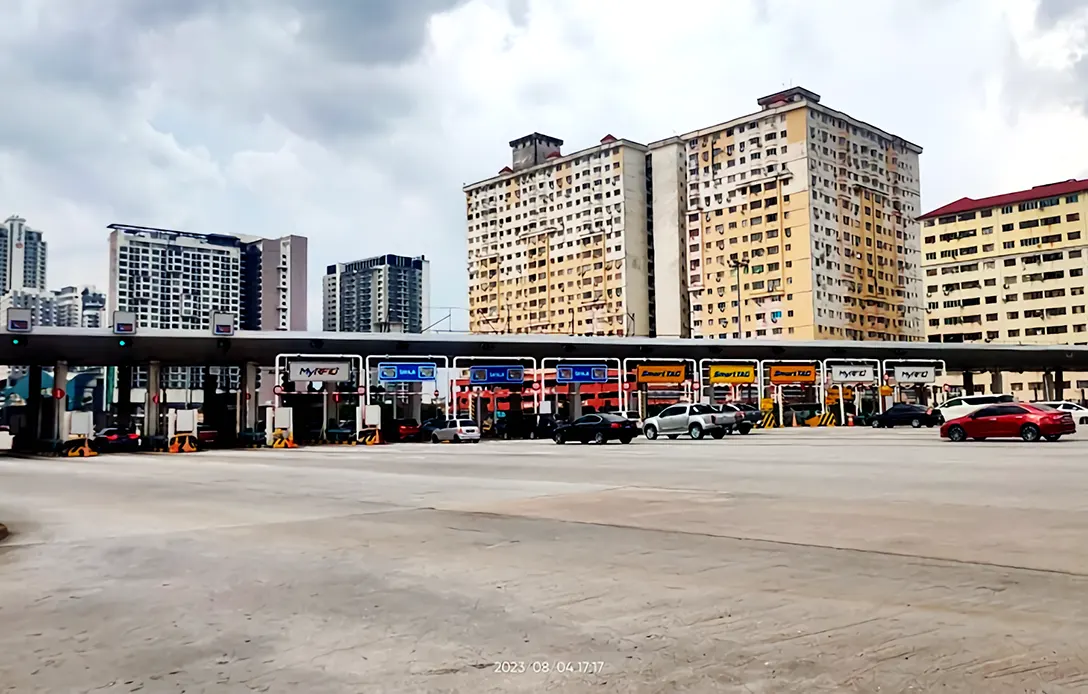

In the late 1990s, Malaysia embraced ETC systems, including the Touch ‘n Go card, allowing vehicles equipped with the card to pass through without stopping.
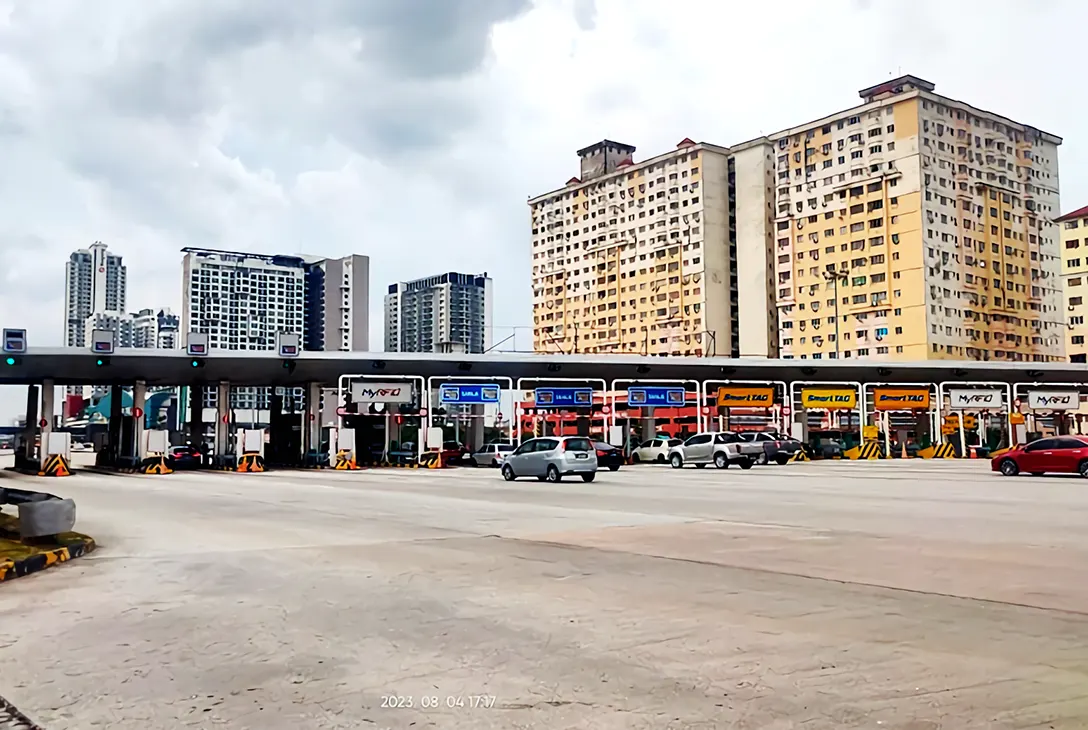

The ETC reduced congestion, improved efficiency, and enhanced the overall travel experience.
With the completion of the North-South Expressway (NSE), the Sungai Besi Toll Plaza became part of this extensive network that connected major cities across Peninsular Malaysia, promoting economic growth and regional development.

This toll plaza served as a critical link between the NSE and Kuala Lumpur and its impact extends beyond toll collection:

The plaza facilitated commerce, trade, and tourism by connecting the southern states to the capital.

It supported industrial zones, residential areas, and commercial centers along its route.
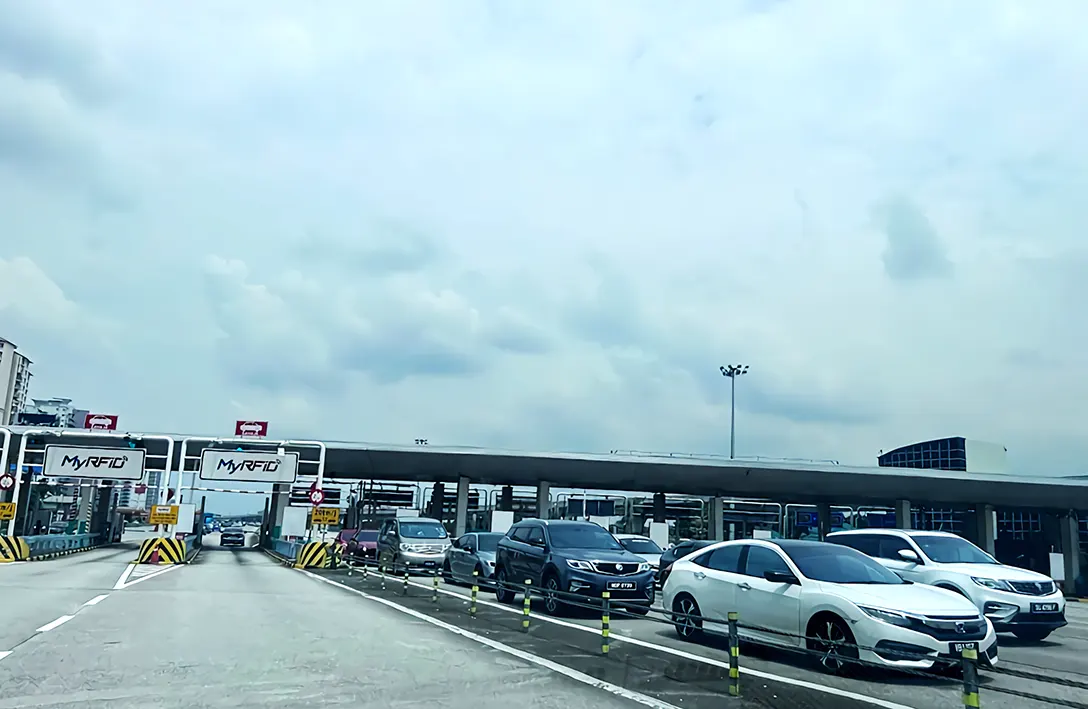

The toll revenue contributed to the overall economic development of the region.
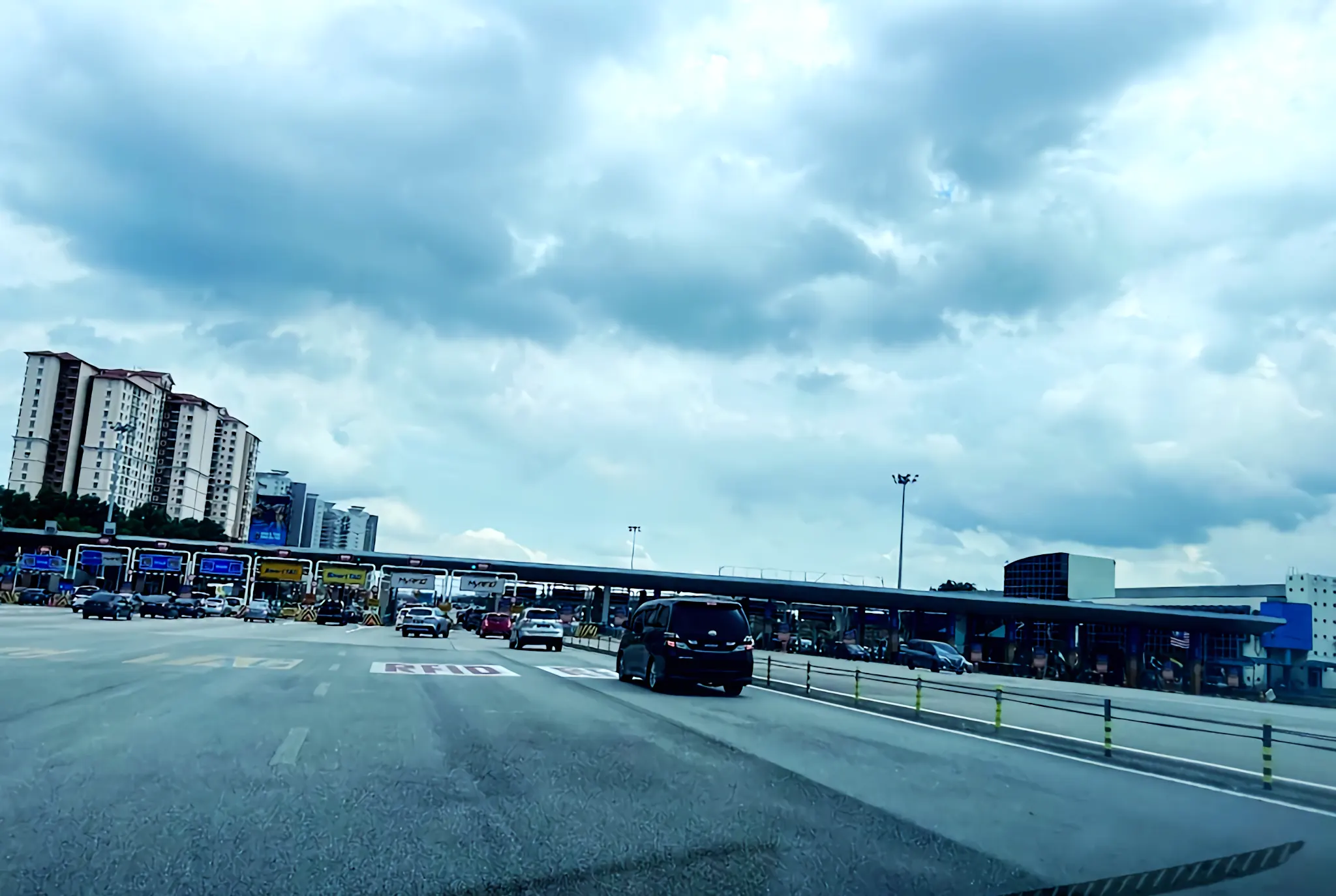

The highway corridor around the plaza witnessed urbanization, with housing developments, commercial hubs, and infrastructure projects and the plaza’s location influenced land use planning, transportation networks, and property values.
The Sungai Besi Toll Plaza symbolizes Malaysia’s commitment to modern infrastructure.
It reflects the nation’s ability to adapt to technological changes and meet the demands of a growing population.

In conclusion, the Sungai Besi Toll Plaza is more than a collection point for toll fees; it represents Malaysia’s journey toward progress, connectivity, and sustainable development.

As the nation continues to evolve, this toll plaza remains a vital link in the intricate web of highways that connect people, places, and possibilities.
North-South Expressway (PLUS Highway) spans approximately 772 kilometers from Bukit Kayu Hitam near the Malaysian-Thai border to Johor Bahru in the southern portion of Peninsular Malaysia and extends to Singapore.
- Senai Utara Toll Plaza, Kulai, Johor
- Bandar Cassia Toll Plaza, Simpang Ampat, Penang
- Bandar Ainsdale Toll Plaza, Labu, Negeri Sembilan
- Nilai toll plaza, Nilai, Negeri Sembilan
- Gurun Toll Plaza, Gurun, Kedah
- Putera Mahkota Toll Plaza, Kajang, Selangor
- Southville City Toll Plaza, Dengkil, Selangor
- Bandar Saujana Putra Toll Plaza, Bandar Saujana Putra, Selangor
- Ayer Keroh Toll Plaza, Alor Gajah, Melaka
- Ipoh Utara Toll Plaza, Ipoh, Perak
★ Driving along the PLUS Highway? Click to check toll charge!